Epiretinal Membrane (ERM)

Close
- Idiopathic or primary epiretinal membrane (ERM) is a relatively common finding, especially in elderly population. Secondary pathomechanisms of ERM development include retinal tears, trauma, vascular occlusions, inflammatory intraocular diseases, ophthalmic procedures including retinal detachment surgery, laser coagulation and cryotherapy of the retina.
- Patients typically complain of blurring of the vision and may also experience metamorphopsia (distortion), aniseikonia (images appearing smaller or larger vs the fellow eye), and, in some cases, diplopia (double vision). Individual symptoms depend on the degree of tractional forces from the epiretinal proliferation at the vitreoretinal interface resulting in distortion of of retinal contour of the foveal region (extrafoveal ERM is typically not symptomatic).
- Depending on the degree of symptomatic visual impairment a surgical intervention with transconjunctival pars plana vitrectomy and membrane peeling may be indicated. Most surgeons recommend simultatnous internal limiting membrabe (ILM peeling) to reduce the likelihood of ERM recurrence.
Synonyms: macular pucker, epiretinal gliosis
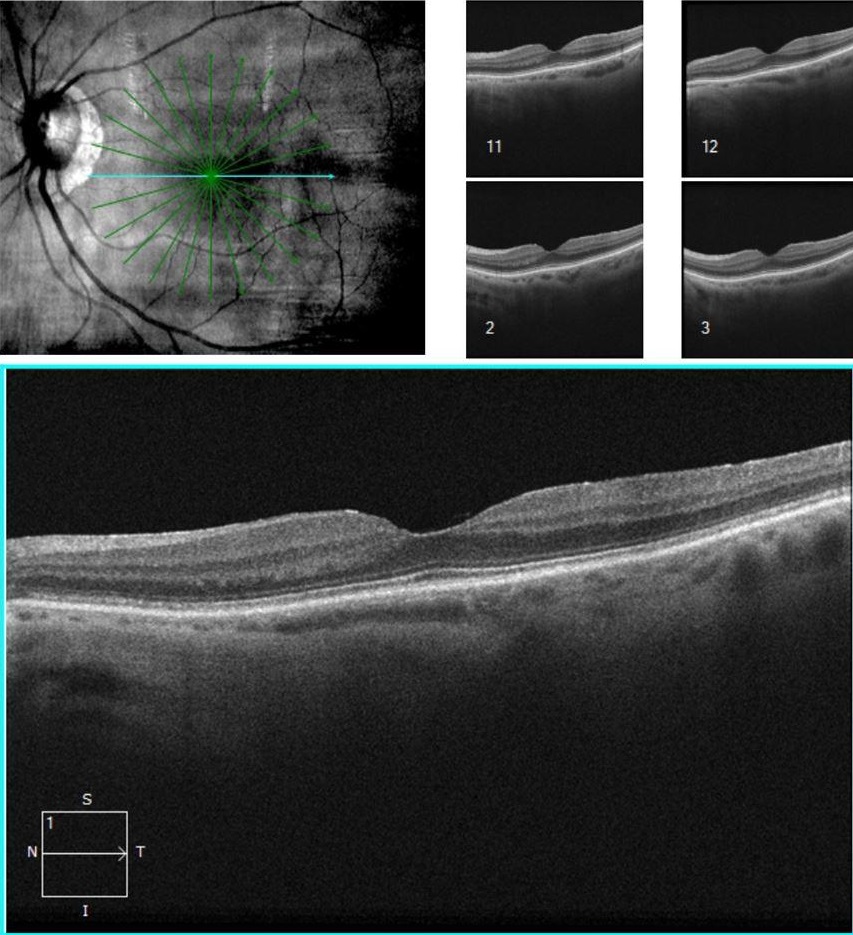
- A pronounced epiretinal membrane with retinal thickening and distortion of the retinal contour and the foveal impression. The patient reported chronic blurry vision for the past 12 months.
Denied metamorphopsia, aniseikonia, or diplopia. BCVA is 20/200. The premacular hyaloid is elevated, but remains attached
at the optic nerve head.
 - OCT - prior to Sx.jfif)
-
Mild extrafoveal ERM that is not causing any significant retinal traction or alteration to the retinal countour. The patient reported no symtpoms and BCVA was 20/20.
The patient was observed with ERM remaining stable over 5 years.
Color fundus photo
Please leave your comments below
Color fundus photo
